Golfer’s elbow
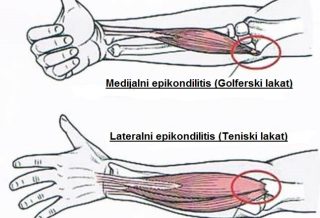
MEDIAL EPICONDYLITIS
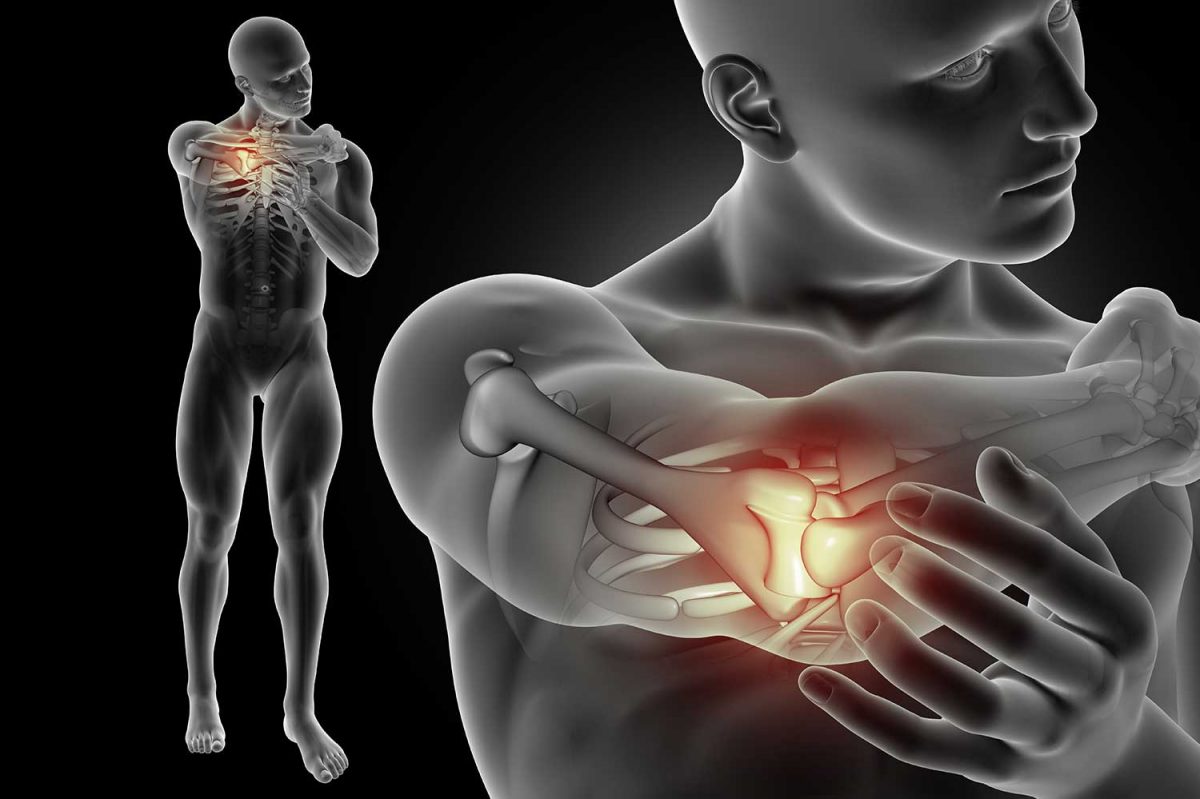
Golf elbow is a condition where there is irritation and inflammation of the tendons of the flexor muscles of the hand and the pronator of the forearm. The main difference between tennis and golf elbow is that in tennis, it occurs on the lateral (outer) side, while in golf it occurs on the medial (inner) side of the elbow. Due to overexertion or overload of the flexion tendons of the wrist and fingers, and especially the tendons of the pronator m.pronator teres. The affected muscles and tendons are located on the inner side of the forearm, they attach to (the medial epicondyle of the humerus), which is why this condition is called medial epicondylitis. Golf elbow most often occurs due to stress, or when the pressure in that zone, as well as in people who often perform non-physiological movements in the elbow, muscle and tendon injuries occur, and thus pain occurs.
CAUSES LEADING TO THE GOLF ELBOW
- Professional golfers
- Racket sports
- Other occupations (painters, hairdressers, lumberjacks)
During a strong extension of the arm at the elbow (extension), while performing a movement of squeezing the hand, there is a strong pull, a group of muscles, which attach to a small area on the inside of the elbow, where the tendon connects with the muscle, or where is attached to the bone, chronic inflammation occurs, which is characterized by pain on touch, or when moving the hand and forearm, in characteristic positions.
Golf elbow is a condition that is less common than tennis elbow, it mostly occurs over the age of 35, although it can be earlier, both men and women are susceptible.
The group more susceptible to golf elbow is:
- Golfers
- Cricket players
- Sports where racket is used
- Basketball
- Bowling
- Apart from athletes, it also occurs in people who are engaged in painting, hammer work, chopping wood, cooking.
The golf elbow develops mostly slowly, although it can be sudden, but it is less frequent, frequent repetition of the arm extension in the elbow in combination with the bending of the hand leads to medial epicondylitis.
GOLFER’S ELBOW SYMPTOMS
- Elbow stiffness as well as pain, weakness when clenching the fist
- Pain on the inside of the elbow, which can spread to the inside of the forearm
- Accompanying weakness and a feeling of helplessness in the hands and joints
- Numbness and tingling in the hands are most sensitive at the level of the little finger as well as the middle finger.
The intensity of the pain itself is very different, it can be said that it is individual, it varies from weak to very strong, if it is not treated, the pain intensifies.
HOW CAN A GOLF ELBOW BE DETERMINED WITH SAFE?
X-ray
MR scan
The test when a physiotherapist or physiatrist resists, while the patient tries to bend the fist, the patient should then feel a sharp pain in the elbow joint.
The patient should avoid flexion movements (bending at the elbow joint), as well as pronation movement (palm facing down), so as not to twist the elbow joint.
Surgical intervention is very rare in golfing elbow, it can be considered only after 6-12 months of active conservative treatment.
RECOMMENDATION OF THE HIRO-PHYSICAL CENTER FOR THE TREATMENT OF THE GOLF ELBOW:
- Cryo massage (ice)
- Electrotherapy set
- Laser
- Manual non-invasive method
- Kinesitherapy (when the pain disappears or is drastically reduced) strengthening the flexors and extensors of the forearm, strengthening and stretching the tendons, the above muscles, restoring flexibility, range of motion, as well as increasing muscle strength.
IF NOT TREATED, IT CAN LEAD TO:
- More intense tissue damage (rupture)
- Chronic pain
- Limited range of mobility
- Permanent contractures (elbow stiffness)
Based on 9 years of work experience, the approximate time for solving the problem of golf elbow, and in our center is 4-6 therapies.
The patient received exercises that he performs later at home.
FOR ALL ADDITIONAL INFORMATION, WE ARE AT YOUR DISPOSAL.
